Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Harvesting Systems: Advancing Regenerative Medicine
The Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Harvesting Systems market was valued at USD 320.00 Million in 2024 and is expected to...
Introduction
Stem cell therapy has emerged as one of the most promising frontiers in modern medicine, offering novel ways to repair, regenerate, and rejuvenate damaged tissues. Among the different stem cell sources, autologous adipose-derived stem cells (ADSCs) have gained remarkable attention for their accessibility, abundance, and therapeutic potential. The development of adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems has made it easier for clinicians to isolate these regenerative cells at the point of care, accelerating their adoption in both clinical practice and research.
Definition
Autologous adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems are medical technologies designed to collect, process, and isolate stem cells from a patient’s own fat tissue (adipose tissue) for therapeutic use. These systems enable minimally invasive extraction, usually via liposuction, followed by specialized processing that separates stem cells from other fat components, ensuring a concentrated, viable cell population. Because the cells are autologous (from the same individual), the risk of immune rejection is minimized, making them valuable in regenerative medicine, tissue repair, and aesthetic procedures.
What Are Adipose-Derived Stem Cells?
Adipose-derived stem cells are mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) found in human fat tissue. Unlike embryonic stem cells, which raise ethical concerns, or bone marrow stem cells, which are difficult to extract, ADSCs provide a practical and patient-friendly alternative.
Key characteristics of ADSCs include:
- Multipotency: They can differentiate into various cell types, such as bone, cartilage, muscle, nerve, and even endothelial cells.
- Immunomodulatory properties: ADSCs can reduce inflammation and modulate immune responses, making them suitable for autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
- Angiogenic potential: They promote the formation of new blood vessels, aiding tissue repair.
- High yield: A small volume of adipose tissue contains a significantly higher concentration of stem cells compared to bone marrow aspirates.
Because fat tissue is both abundant and relatively easy to obtain through minimally invasive procedures like liposuction, ADSCs are considered an ideal source for autologous regenerative therapies.
Why Autologous Stem Cells?
The term autologous refers to stem cells harvested from the same patient who will receive the therapy. This approach offers distinct advantages over allogeneic (donor-derived) therapies:
- Reduced Risk of Immune Rejection: Since the cells originate from the patient, there is no risk of graft-versus-host disease or rejection.
- Ethical Acceptability: Autologous sources avoid the ethical debates surrounding embryonic stem cells.
- Immediate Availability: Harvesting and processing can often be done in a same-day procedure.
- Personalized Medicine: Cells are tailored to the patient’s biology, ensuring compatibility.
These benefits explain why autologous ADSC harvesting systems are becoming a cornerstone of point-of-care regenerative solutions.
The Science of Harvesting ADSCs
Adipose tissue is obtained through a liposuction procedure, often performed under local anesthesia. The harvested fat contains a mixture of mature adipocytes, blood, extracellular matrix, and a population of stem cells. To isolate ADSCs, the tissue must be processed to extract the stromal vascular fraction (SVF), which contains the regenerative stem and progenitor cells.
Steps in the Harvesting Process:
- Fat Collection – Adipose tissue is gently aspirated using a cannula.
- Processing and Separation – Specialized systems process the tissue to remove unwanted components (blood, oil, connective tissue).
- Stem Cell Isolation – The SVF is separated, containing ADSCs and other regenerative cell populations.
- Preparation for Use – The isolated ADSCs can then be re-injected into the patient at the site of injury, disease, or aesthetic concern.
Manual methods for ADSC isolation are labor-intensive and require lab-grade equipment. This is where automated harvesting systems bring game-changing advantages.
Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Harvesting Systems
Over the past decade, biotechnology companies have introduced innovative closed-system devices that allow clinicians to harvest, isolate, and prepare ADSCs in a sterile and efficient manner. These systems are designed for use in clinical settings such as hospitals, outpatient surgery centers, and regenerative medicine clinics.
Key Features of Harvesting Systems:
- Closed, Sterile Environment – Minimizes contamination risk and maintains cell viability.
- Automated Processing – Reduces human error and speeds up the procedure.
- Point-of-Care Application – Enables same-day treatment without the need for external laboratories.
- Standardization – Ensures consistent quality and reproducibility of results.
Some systems employ enzymatic digestion (using collagenase) to break down the extracellular matrix and release ADSCs, while others rely on mechanical separation techniques like centrifugation, filtration, or ultrasonic disruption.
Clinical Applications of ADSCs
Autologous adipose-derived stem cells are already being investigated and applied across a wide range of therapeutic areas:
Orthopedics:
- Treatment of osteoarthritis, cartilage injuries, and tendon tears.
- Promotes regeneration of musculoskeletal tissues.
Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery:
- Fat grafting procedures for facial rejuvenation, breast reconstruction, and scar repair.
- Enhanced survival of fat grafts due to the regenerative properties of ADSCs.
Dermatology & Aesthetics:
- Skin rejuvenation, hair restoration, and wound healing.
- Improvement in elasticity, texture, and scar reduction.
Cardiovascular Disorders:
- Early trials show ADSCs may aid in repairing ischemic heart tissue.
Neurology:
- Potential applications in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and multiple sclerosis, though research is still in its infancy.
Chronic Inflammatory Conditions:
- ADSCs’ immunomodulatory abilities make them candidates for conditions like Crohn’s disease or rheumatoid arthritis.
Advantages Over Traditional Stem Cell Sources
Compared to bone marrow-derived stem cells (BM-MSCs), ADSCs offer several practical and clinical advantages:
- Higher Stem Cell Yield: Up to 500 times more stem cells per gram of tissue.
- Less Painful Harvesting: Liposuction is far less invasive than bone marrow aspiration.
- Shorter Recovery Time: Fat harvesting is minimally invasive, reducing downtime.
- Broader Patient Suitability: Almost everyone has excess adipose tissue, whereas bone marrow quality declines with age.
These benefits make autologous adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems particularly attractive for clinics looking to provide regenerative therapies efficiently.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite their promise, ADSC harvesting systems face certain challenges:
- Regulatory Hurdles – Different countries regulate stem cell therapies differently. Enzymatic digestion methods, for instance, are more strictly controlled in some regions.
- Standardization – Variability in harvesting techniques can affect stem cell yield and quality.
- Long-Term Safety Data – While generally safe, more longitudinal studies are needed to confirm safety across a wide range of applications.
- Cost – Advanced harvesting systems can be expensive, limiting accessibility in smaller clinics.
Future Directions in ADSC Harvesting
The next generation of adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems is focusing on:
- Fully Automated, Cartridge-Based Systems: Simplifying the process for clinicians and reducing training requirements.
- Point-of-Care Biomanufacturing: Enabling not only harvesting but also expansion and cryopreservation directly in clinical settings.
- Combination Therapies: Integrating ADSCs with platelet-rich plasma (PRP), scaffolds, or biomaterials for enhanced regenerative outcomes.
- Artificial Intelligence and Data Integration: Leveraging AI to optimize yield predictions, patient selection, and treatment protocols.
With the global market for stem cell therapy projected to grow significantly in the coming decade, ADSC harvesting systems are set to become indispensable tools in regenerative healthcare.
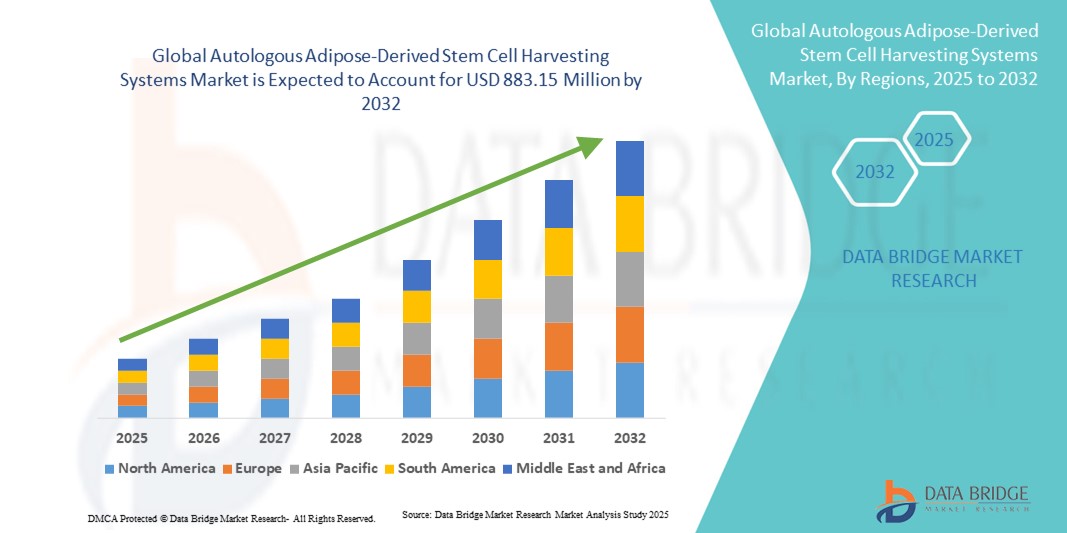
Growth Rate of Autologous Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Harvesting Systems Market
According to Data Bridge Market Research, the autologous adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems market was estimated to be worth USD 320 million in 2024 and is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 13.53% to reach USD 883.15 million by 2032.
Conclusion
Autologous adipose-derived stem cell harvesting systems represent a paradigm shift in regenerative medicine. By providing a reliable, abundant, and patient-friendly source of stem cells, they have unlocked new possibilities in orthopedics, plastic surgery, dermatology, and beyond.