Top Medications That Help Reduce Stomach Acid Quickly
Stomach acid is vital for digestion, but when produced in excess, it can lead to discomfort and various gastrointestinal issues...
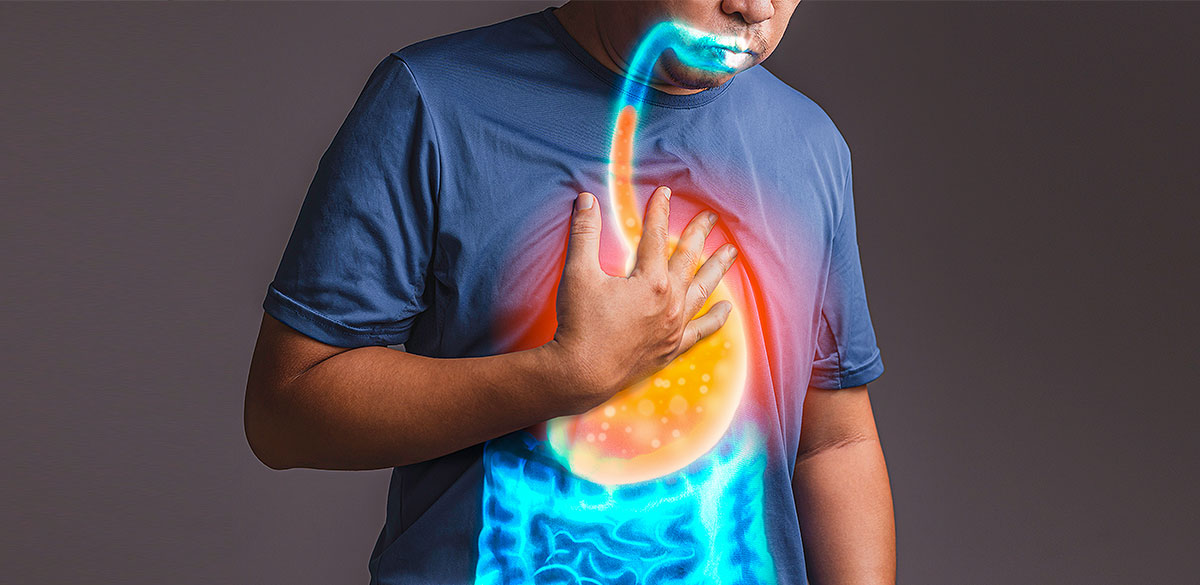
Stomach acid is vital for digestion, but when produced in excess, it can lead to discomfort and various gastrointestinal issues such as heartburn, acid reflux, gastritis, and even ulcers. Fortunately, several medications are available to help reduce stomach acid quickly and effectively. One of the most well-known and previously widely used options is ranitidine 150 mg, along with others like proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) and antacids.
Understanding Excess Stomach Acid
The stomach naturally produces hydrochloric acid (HCl) to help break down food. However, when this acid is overproduced or improperly managed, it can lead to:
- Heartburn
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD)
- Peptic Ulcers
- Bloating and discomfort
In such cases, medications become essential for symptom relief and healing.
1. Ranitidine 150 mg: The H2 Blocker
Ranitidine 150 mg, commonly known by the brand name Zantac (now discontinued in some countries), is an H2-receptor antagonist. It works by blocking histamine on the cells in the stomach lining, reducing acid production.
Benefits of Ranitidine 150 mg:
- Fast relief from heartburn and indigestion
- Effective in treating and preventing ulcers
- Often used for nighttime acid suppression
While Ranitidine was pulled from the market in some countries due to concerns about potential impurities, generic versions are still available in many regions under strict quality controls. Always consult your healthcare provider before use.
2. Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs)
PPIs are among the most effective medications for reducing stomach acid. They work by blocking the enzyme in the stomach wall responsible for acid production.
Common PPIs:
- Omeprazole
- Esomeprazole
- Pantoprazole
- Lansoprazole
Advantages of PPIs:
- Long-lasting relief (up to 24 hours)
- Ideal for chronic GERD
- Help heal esophageal and stomach lining damage
PPIs are usually taken before meals and may take a few days to show full effects, but they are superior for long-term management.
3. Antacids: Instant, Short-Term Relief
Antacids neutralize existing stomach acid quickly. They are available over the counter and are often the first line of defense against mild heartburn.
Popular Antacids:
- Calcium carbonate (Tums)
- Magnesium hydroxide (Milk of Magnesia)
- Aluminum hydroxide
Pros:
- Immediate relief
- Good for occasional use
- Affordable and accessible
Cons:
- Short duration of action
- Not suitable for long-term control
- Can cause constipation or diarrhea depending on the formulation
4. H2 Blockers (Other Than Ranitidine)
If Ranitidine isn’t available, other H2 blockers can serve as effective substitutes:
- Famotidine (Pepcid) – Considered safer and widely used.
- Cimetidine (Tagamet) – Older, with some drug interaction concerns.
These drugs work similarly to ranitidine and are helpful for moderate acid issues and nighttime relief.
Choosing the Right Medication
When selecting a medication for acid relief, consider the following:
- Frequency of symptoms: Occasional heartburn may only require antacids.
- Chronic issues: GERD and ulcers often need PPIs or H2 blockers.
- Medical history: Some drugs interact with other medications or may not be safe for kidney or liver conditions.
- Availability: Ranitidine 150 mg may be available under specific brands and regulations.
Note: Long-term use of acid reducers, especially PPIs, should be monitored by a doctor due to potential risks like nutrient deficiencies or kidney issues.
Final Thoughts
If you’re suffering from frequent stomach discomfort, it’s crucial to address it early. Medications like Ranitidine 150 mg, PPIs, and antacids each have a role in managing stomach acid, depending on the severity and frequency of your symptoms.